Let’s face it: we live in an illusion. That is to say, modern theories of cognition demonstrate that we do not really see what is around us. Instead, our eyes dart from one detail to the next to construct a convincing model of the world. Then we base our decisions on this model. Moreover, we are oblivious to the basic brain mechanisms that govern our actions, a phenomenon that you may have noticed when emerging from your thoughts and finding yourself in a place without remembering how you got there.
While this marvel of biology lets us accomplish great things, it also proves unreliable on many occasions. The mental structure of a mistake is “I thought that … but …,” and we make lots of them. For example, “I thought the department store was open on Sundays, but it was closed when I arrived,” or “I thought that batteries were included when I bought a clock, but they were not, and I was not able to use it when I got home.”
Mistakes are not restricted to our personal lives, of course. A typical workday is littered with errors, small and large. And this is why lean is so brilliant: It is a complete business strategy based on rooting out and fixing our misconceptions. But what does that mean in practice?
Most people interested in lean are familiar with the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle. However, a common misconception about this method is that its main purpose is to improve processes. The logic goes like this: You find a problem, discover a missing standard, fix it, and then train everybody to use it. While this understanding is not wrong per se, it can lead to an environment where people are expected to follow too many processes without understanding why they are doing it — a dangerous situation if the company operates in a changing environment.
A better way to understand PDCA is to look at it as a means to root out misconceptions and fix the glitches in our thinking.
A better way to understand PDCA is to look at it as a means to root out misconceptions and fix the glitches in our thinking.
Let’s take an example. Users of a web application are complaining that pages are taking too long to load. By responding to a few “why’s,” one can easily get closer to the root of the technical problem:
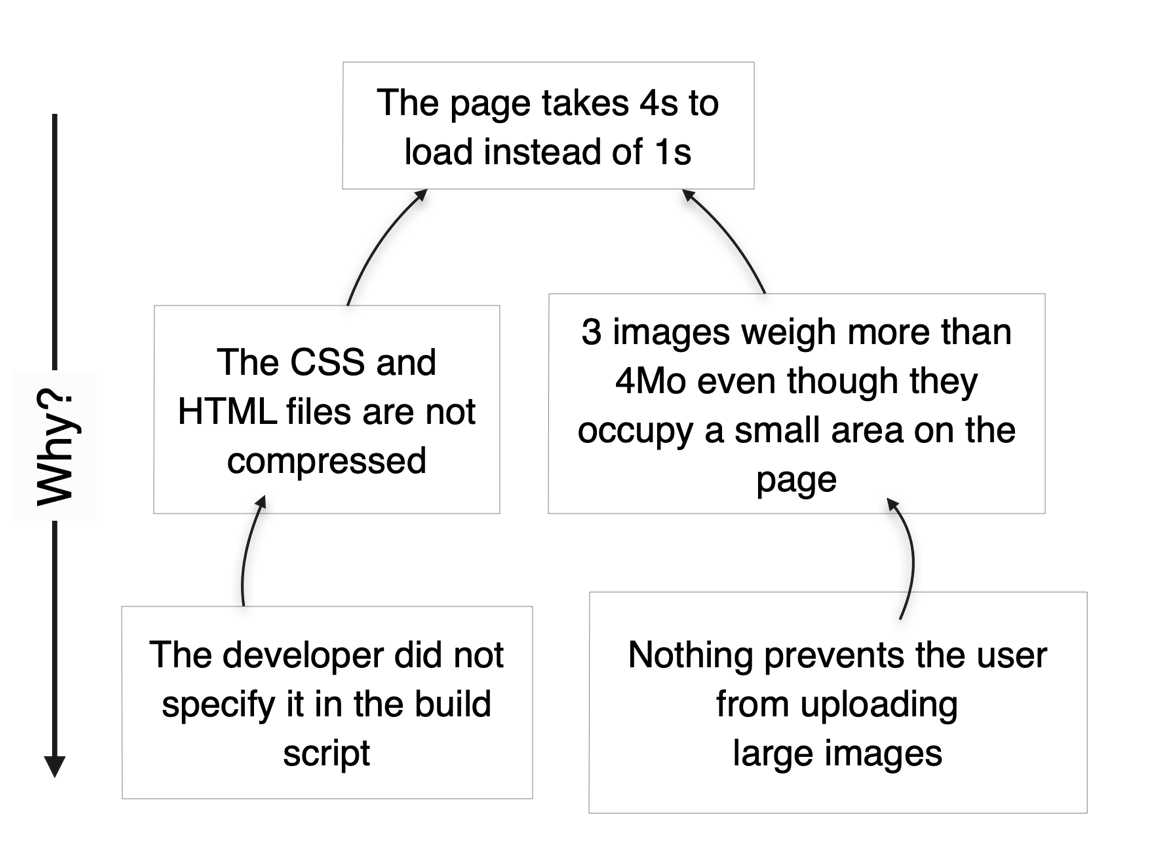
While we should certainly delve deeper into the technical details to find the specific point of change to fix the issue, let’s remain at this level for the sake of argument — because we can already infer that we will end up with two kinds of countermeasures:
- Fix the build script so that CSS and HTML files are compressed and load faster.
- Add a check or warning to prevent users from uploading images larger than 1Mo, or better yet, transform the uploaded files automatically without burdening users with extra work.
The problem would probably be fixed either way, but we wouldn’t have actually learned much. We can expect the same people, and the same company, to repeat the same kind of mistakes in the future.
A better way to guide our search for root causes consists in trying to answer the question:
What is the mistake we keep repeating that creates this problem?
In our example, this could look like this:
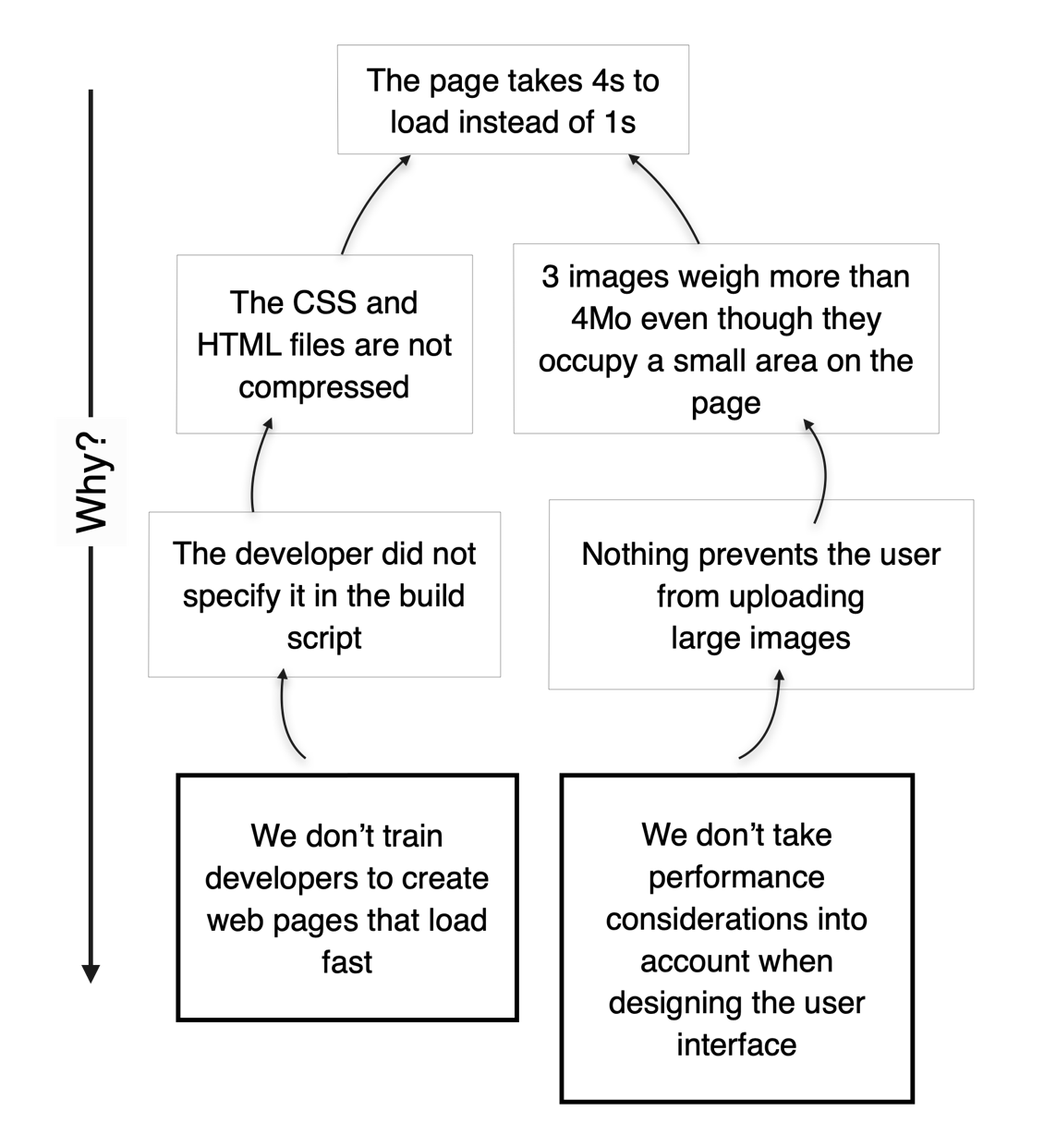
By using this approach, learning can occur because it makes us aware of the shortcomings of our mental models. However, this is only the beginning.
By solving problems repeatedly in a given area, we can explore the factors that influence performance and progressively build a model of these factors. In our example, this approach would look like this:
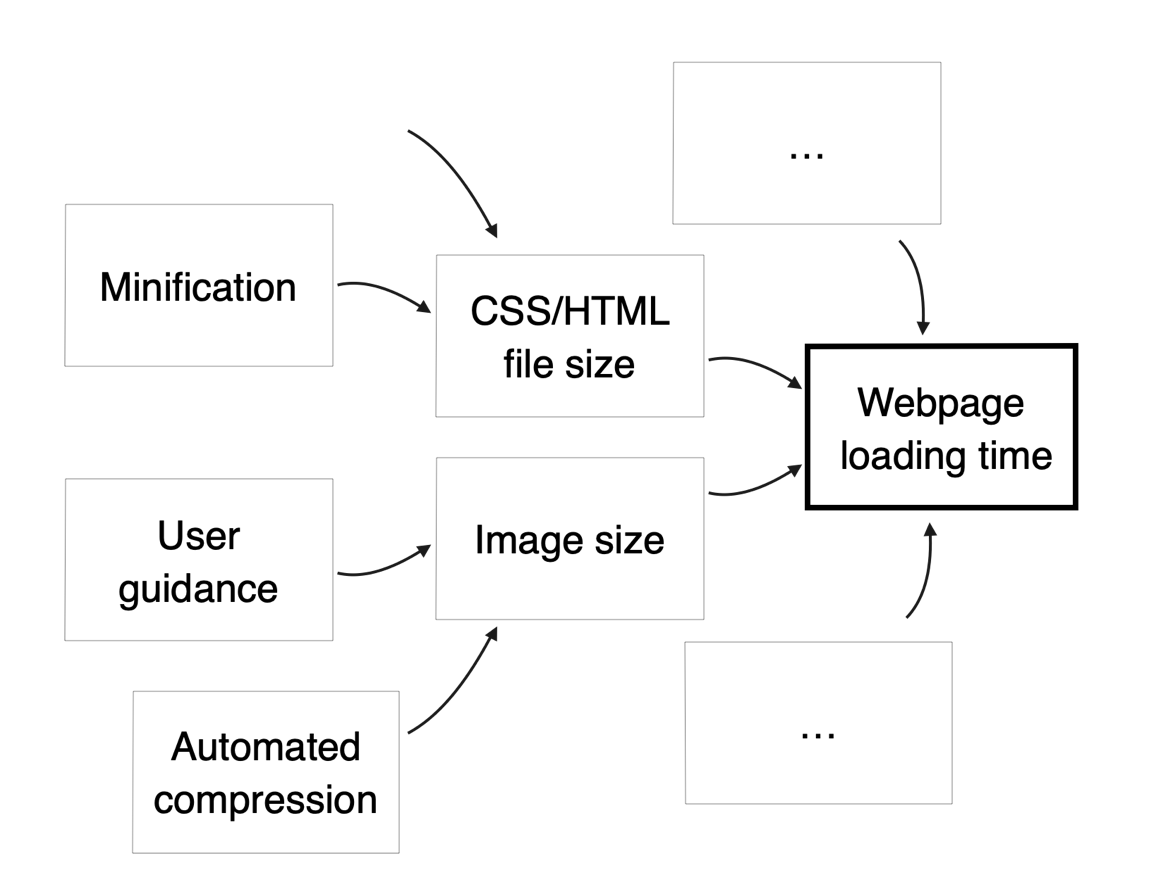
This model can then be taught, discussed, and extended because it’s a standard: a collection of knowledge points that serve as a basis for training and reflection.
Ultimately, the goal of problem-solving is not just to fix tools and processes.
By creating standards, a company can deliberately build expertise in any domain. When done on topics that directly relate to customer preferences, and when performed by everybody every day, this creates a dynamic in which people are always building knowledge and changing to adapt to customer needs, which is the essence of the lean strategy.
Ultimately, the goal of problem-solving is not just to fix tools and processes. Instead, it is a unique opportunity to think about how we think and develop expertise where it counts. In addition, it is a robust, hands-on formula to create a company that keeps adapting to changing market conditions and creates value for society over decades.
Problem Framing Skills
Improve your ability to break down problems into their specific, actionable parts.





